
Dr. Waseem Abbas
Cancer Treatment Specialist
Director Research, Max Hospital, Shalimar Bagh
How to contact me
Max Superciality Hospital, FC 50, C and D Block, Shalimar Place Site, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi, Delhi 110088
Phone: +91 98112 42729
Email: drabbasdoc@gmail.com
Search this website
Common Cancers in India
Get a free E-consultation about lung cancer immunotherapy in Delhi
Neuroendocrine tumors are a group of uncommon tumors that start in specialized cells in your neuroendocrine system. These cells combine the traits of nerve cells and hormone-producing endocrine cells. They link your endocrine system, which manages your hormones, and your nervous system. Neuroendocrine cells are scattered throughout your body.
NET has several types and sub-types with symptoms that might be mistaken for other less serious conditions. Once considered a rare cancer, more and more people are being diagnosed with NET thanks to improved diagnostic tests that identify NET more quickly. Early diagnosis and treatment continues to increase the number of people living for years with NET.
What are the different types of neuroendocrine tumors?

Neuroendocrine tumors are classified as primary or secondary tumors. A primary tumor is cancer that hasn’t spread to other areas of your body. A secondary tumor is a NET that has spread, usually to your lymph nodes in your lymphatic system, your liver or your bones.
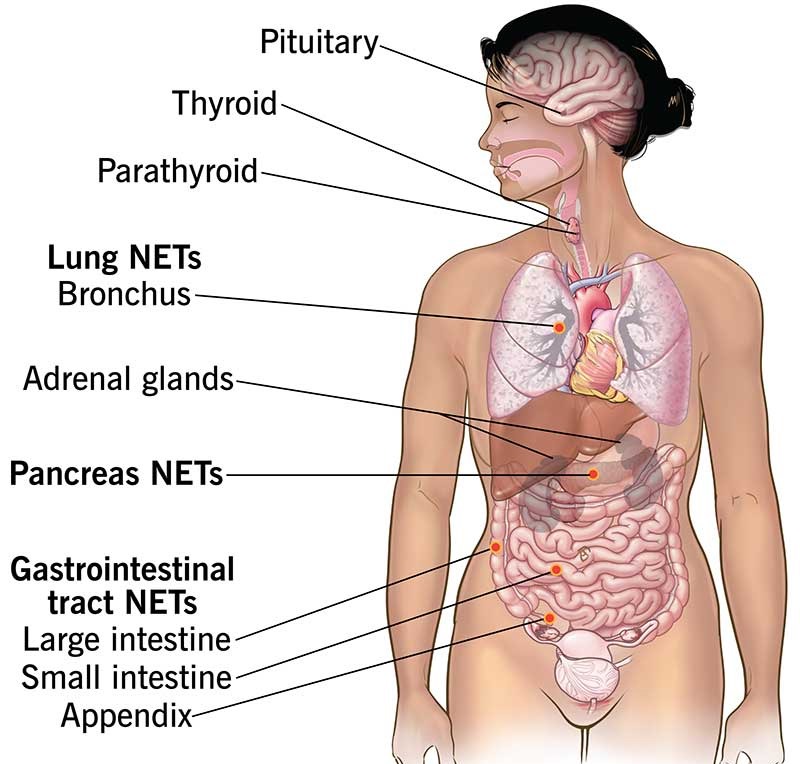
NET types are based on their location. For example, a neuroendocrine tumor in your gut is a neuroendocrine tumor of the gastrointestinal tract. Here are the most common primary neuroendocrine tumor types:
Gastrointestinal (GI) tract. NETs develop most commonly in the GI tract, specifically in the large intestine (20%), small intestine (19%), and appendix (4%). The GI tract plays a central role in digesting foods and liquid and in processing waste. GI tract NETs used to be called carcinoid tumors.
Lung. The lung is the second most common location of NETs. About 30% of NETs occur in the bronchial system, which carries air to the lungs. Lung NETs also used to be called carcinoid tumors.
Pancreas. Approximately 7% of NETs can develop in the pancreas, a pear-shaped gland located in your abdomen between the stomach and the spine. Pancreas NETs (PNETS), which used be called islet cell tumors, represent about 7% of all pancreatic cancers.
What are the symptoms of neuroendocrine tumors?
Neuroendocrine tumor symptoms vary based on the location of the cancerous cells. That being said, a condition called carcinoid syndrome is a symptom for neuroendocrine carcinoma of the gastrointestinal tract (GI NETs) and NETs of the lung. Like many forms of cancer, not all symptoms mean you have cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider if you notice changes in your body that are similar to symptoms listed below.
Understanding the staging and grading process might be helpful information as you and your provider discuss treatment plans.
What are NETs grades?
Grade 1 (low-grade tumor): These cells divide at a low rate and are growing slowly.
Grade 2 (intermediate-grade tumor): These cells divide at an intermediate rate.
Grade 3 (high-grade tumor): These cells divide at a fast rate and therefore grow quickly.
How are neuroendocrine tumors treated?
Surgery is the most common treatment for NET. If your tumors are large or have spread, other treatments might be:

Somatostatin analogs: Somatostatin analogs are a type of treatment that may stop your body from making too many hormones. This may slow down the growth of the tumor when cancer cells have spread to other part of the body.
Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs that target certain genes or proteins to kill cancer cells.
Chemotherapy: This treatment uses several types of drugs to kill cancer cells.
