
Dr. Waseem Abbas
Cancer Treatment Specialist
Director Research, Max Hospital, Shalimar Bagh
How to contact me
Max Superciality Hospital, FC 50, C and D Block, Shalimar Place Site, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi, Delhi 110088
Phone: +91 98112 42729
Email: drabbasdoc@gmail.com
Search this website
Common Cancers in India
Get a free E-consultation about lung cancer immunotherapy in Delhi
Immunotherapy for breast cancer treatment in Delhi. India

Patient information and resources
Immunotherapy definition
Immunotherapy activates body’s own immune system to fight cancer. It kills the chemotherapy resistant cells. Immunotherapy activates T Cell as in our body which attack the cancer cells and kill them.
Usually breast cancer cells are resistant to immunotherapy and and it works for triple negative breast cancer and now emerging data has shown that immunotherapy also works in Her2 neu positive breast cancer.
It is a new hope for patients suffering from Triple negative breast cancer especially when used early.
Immunotherapy should be used early in breast cancer and not at in late stages.
How it may treat breast cancer?
Cells in the body contain proteins called immune checkpoints. These immune system regulators signal that cells are healthy.
Immune checkpoints allow the immune system to fight infected or diseased cells while preventing it from attacking healthy tissues.
The immune system is complex and involves different types of cells, including T cells, which circulate the body checking for disease or infection. These specialized cells examine other cells to identify immune checkpoints.
If the immune system does not recognize proteins within cells, it attacks them. This process is essential in allowing the body to fight diseases and infections.
Immune check point inhibitors
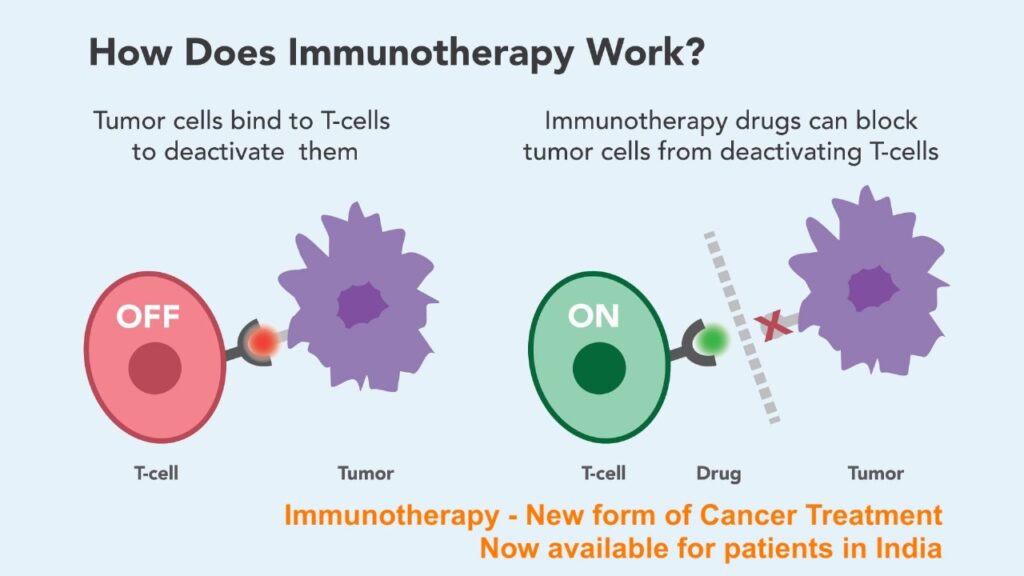
These are drugs which act against CTLA-4, PDL-1 and PD-1 proteins and block them to relieve the inhibitory signals on immune cells.
e.g
Atezolizumab- This drug was first approved for metastatic triple negative breast cancer which is PDL 1 positive by IHC 142. Now it is showing efficacy against early triple negative breast cancer as well and can be used upfront with immunotherapy as a part of neo adjuvant protocol.
Tecentriq inhibits PD-L1 proteins, and doctors may use it to treat:
- metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)
- PD-L1-positive breast cancer
- locally advanced breast cancer where surgery is not effective
Pembrolizumab – This drug has also shown efficacy against triple negative breast cancer in early stages.
Keytruda
Keytruda inhibits PD-1 proteins. Doctors may use Keytruda alongside chemotherapy to target triple-negative breast cancer that has spread to other areas of the body or has returned locally and is not treatable with surgery.
Nivolumab – is the another drug which has shown efficacy in triple negative breast cancer.
Effectiveness
Lot of questions are being asked by experts and patients about the efficacy of immunotherapy in breast cancer treatment. Initially it did not work, but what we saw we need to combine it with chemotherapy and use at early stages for TNBC.
Which people with breast cancer will be most likely to benefit from immunotherapy?
Researchers are starting to get some clues from clinical trials about who immunotherapy is most likely to help. For example, people with triple-negative breast cancer may get more benefit from immunotherapy than people with other subtypes of breast cancer. Immunotherapy may be more likely to work in people whose breast cancer has more GENE MUTATIONS whose tumor cells have higher levels of a protein called PD-L1. In addition, there is some information that suggests immunotherapy may work better if it is given early during treatment.
In late 2018, results from a breast cancer immunotherapy clinical trial were PUBLISHED IN New England Journal of Medicine. The study examined adding atezolizumab to a standard chemotherapy drug called protein-bound paclitaxel in people with metastatic, triple-negative breast cancer who had not previously received treatment for their cancer. Researchers found that adding immunotherapy to the chemotherapy drug may be beneficial for a subset of people, although it increases harmful side effects, also called toxicity. In addition, the findings support the clues found in other clinical trials about who may most benefit from immunotherapy. This treatment combination was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in March 2019. More research is needed to determine which cancers are most likely to respond to the combination.
Should immunotherapy be tried if a breast cancer has not responded to multiple standard treatments?
Unfortunately, studies of immunotherapy for breast cancer that is resistant to multiple prior treatments have not shown much benefit for the vast majority of people. However, there are hints that immunotherapy will eventually play a role in treating breast cancer.
Possible side effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors
Side effects of these drugs can include fatigue, cough, nausea, skin rash, poor appetite, constipation, and diarrhea.
Other, more serious side effects occur less often.
Infusion reactions: Some people might have an infusion reaction while getting these drugs. This is like an allergic reaction, and can include fever, chills, flushing of the face, rash, itchy skin, feeling dizzy, wheezing, and trouble breathing. It’s important to tell your doctor or nurse right away if you have any of these symptoms while getting these drugs.
Autoimmune reactions: These drugs remove one of the safeguards on the body’s immune system. Sometimes the immune system starts attacking other parts of the body, which can cause serious or even life-threatening problems in the lungs, intestines, liver, hormone-making glands, kidneys, or other organs.
It’s very important to report any new side effects to your health care team quickly. If serious side effects do occur, treatment may need to be stopped and you may get high doses of corticosteroids to suppress your immune system.
