
Dr. Waseem Abbas
Cancer Treatment Specialist
Director Research, Max Hospital, Shalimar Bagh
How to contact me
Max Superciality Hospital, FC 50, C and D Block, Shalimar Place Site, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi, Delhi 110088
Phone: +91 98112 42729
Email: drabbasdoc@gmail.com
Search this website
Common Cancers in India
Get a free E-consultation about lung cancer immunotherapy in Delhi
Immunotherapy for blood cancer lymphoma, and hematological malignancies in Delhi/India – Patient education and resources

Many blood cancers are systemic diseases that involve primary and secondary lymphoid organs and they all arise from immune cells. Unlike solid tumors where only a few lymphocytes are present, blood cancer involves continuously and systemic contact between the tumor clone and the immune system.
In modern medicine one of the oldest forms of immunotherapy would be allogenic stem cell transplantation. It cures cancer because of Graft vs Host disease (GVT)
Immunotherapy is a new tool to fight cancer and has changed our way how we look at treatment of relapsed cancer or difficult to treat cancer.
Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma -Hodgkins lymphoma was the first blood cancer where immunotherapy showed very good results. It showed hope where it was lost. And with time we saw more and more patients surviving longer. Is has become the standard of care for patients who relapse after standard treatment.
Leukemia
There are four main types of leukemia, each named for the rate at which the disease develops and worsens as well as the affected blood cell type.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): fast-growing cancer that starts in myeloid cells—the precursor to red blood cells, platelets (cells that clot the blood), or white blood cells known as granulocytes; also known as acute myelogenous or myeloblastic leukemia.
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): slower-growing cancer that starts in myeloid cells—the precursor to red blood cells, platelets (cells that clot the blood), or white blood cells known as granulocytes; also known as chronic myelogenous or myeloblastic leukemia.
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL): fast-growing cancer that starts in lymphoid cells, which make different types of white blood cells; also known as acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): slower-growing cancer that starts in lymphoid cells, which make different types of white blood cells; also known as chronic lymphoblastic leukemia.
Treatment
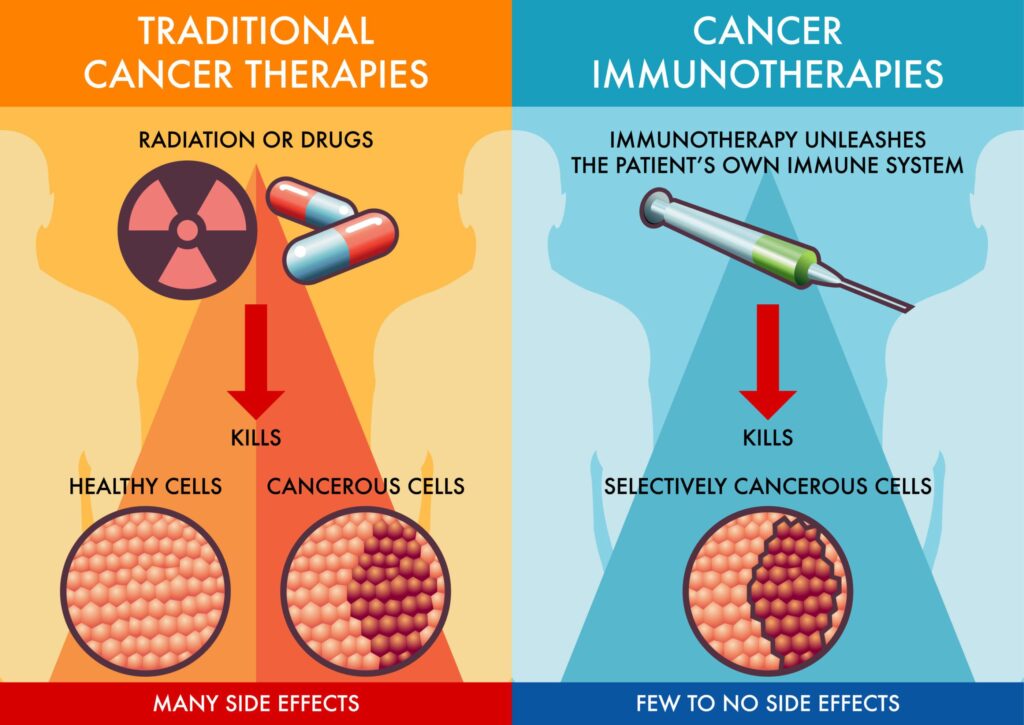
Targeted Antibodies-Different targeted anti bodies are available for the treatment of leukemias apart from chemotherapy
Alemtuzumab (Campath®): a monoclonal antibody that targets the CD52 pathway; approved for subsets of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
Blinatumomab (Blincyto®): a bispecific antibody that targets CD19 on tumor cells as well as CD3 on T cells; approved for subsets of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin (MyloTarg®): an antibody-drug conjugate that targets the CD33 pathway and delivers toxic drugs to cancer cells; approved for subsets of adult and pediatric patients with CD33-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Inotuzumab ozogamicin (Besponsa®): an antibody-drug conjugate that targets the CD22 pathway and delivers toxic drugs to cancer cells; approved for subsets of patients with advanced acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Obinutuzumab (Gazyva®): a monoclonal antibody that targets the CD20 pathway; approved for subsets of patients with CD20-positive chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), including as a first-line therapy
Ofatumumab (Arzerra®): a monoclonal antibody that targets the CD20 pathway; approved for subsets of patients with CD20-positive chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), including as a first-line therapy
Rituximab (Rituxan®): a monoclonal antibody that targets the CD20 pathway; approved for subsets of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), including as a first-line therapy
Adoptive Cell Therapy
Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah®): a CD19-targeting CAR T cell immunotherapy; approved for subsets of children and young adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Immunomodulators
Interferon alfa-2a: a cytokine that targets the IFNAR1/2 pathway; approved for subsets of patients with hairy cell leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
Interferon alfa-2b (Intron A®): a cytokine that targets the IFNAR1/2 pathway; approved for subsets of patients with hairy cell leukemia and aggressive follicular non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Acute leukemias are very aggressive blood cancers and one they relapse after allogenic bone marrow transplant few options are lest and majority of patients go for palliative care. Treatment of such patients with immunotherapy is evolving and so far very less data is available and not much research in this field. But some research is available and that has shown promising results. Immunotherapy at present is not recommended for patients of acute leukemia and should only be used in the context of clinical trial.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Immune system cells normally have substances that act as checkpoints to keep them from attacking other healthy cells in the body. Cancer cells sometimes take advantage of these checkpoints to avoid being attacked by the immune system.
Drugs such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) work by blocking these checkpoints, which can boost the immune response against cancer cells. Pembrolizumab can be used to treat primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) that has not responded to or has come back after other therapies.
What if the future of check point inhibitors in Blood cancer?
In Hodgkin’s lymphoma Immunotherapy has shown excellent responses. Second immune check point inhibitors are available for the treatment of primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma. In other forms of blood cancer, it has shown promise and research is going on and soon we will have result of these trials.
Immunotherapy should be administered under the supervision of experts in this field.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Immune system cells normally have substances that act as checkpoints to keep them from attacking other healthy cells in the body. Cancer cells sometimes take advantage of these checkpoints to avoid being attacked by the immune system.
Drugs such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) work by blocking these checkpoints, which can boost the immune response against cancer cells. Pembrolizumab can be used to treat primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) that has not responded to or has come back after other therapies.
Not to mention about CAR T Therapy
In this treatment, immune cells called T cells are removed from the patient’s blood and altered in the lab to have specific receptors (called chimeric antigen receptors, or CARs) on their surface. These receptors can attach to proteins on the surface of lymphoma cells. The T cells are then multiplied in the lab and given back into the patient’s blood, where they can seek out the lymphoma cells and launch a precise immune attack against them.
Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah, also known as tisa-cel) is approved to treat people with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, high grade B-cell lymphoma, and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arising from follicular lymphoma, after trying at least two other kinds of treatment.
Lisocabtagene maraleucel (Breyanzi, also known as liso-cel) is approved to treat adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, high grade B-cell lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma grade 3B, after at least two other kinds of treatment have been tried.
Brexucabtagene autoleucel (Tecartus, also known as brexu-cel) is approved to treat adults with mantle cell lymphoma that has come back or is no longer responding to other treatments.
Research
- https://www.cureus.com/articles/17222-harnessing-the-immunomodulatory-effects-of-radiation-in-urinary-bladder-cancer#:~:text=Extensive%20preclinical%20data%20supports%20the,the%20systemic%20anti%2Dtumor%20effect.
- https://www.ojionline.org/article.asp?issn=2589-1871;year=2020;volume=4;issue=3;spage=110;epage=114;aulast=Patil
- https://ijmio.com/cardiotoxicity-in-patients-on-trastuzumab-in-her2-positive-breast-cancer-a-retrospective-analysis-from-a-center-in-north-india/
- https://www.crstonline.com/article.asp?issn=2590-3233;year=2020;volume=3;issue=1;spage=146;epage=147;aulast=Abbas
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343512692_Predictors_of_Occult_Neck_Metastasis_and_Extra_Capsular_Spread_in_Early_Oral_Cancers
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30050778/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31607695/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31807489/
- https://www.proquest.com/openview/d26bb79fb4948a5db6724295f88156a5/1.pdf?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=226512
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31489291/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6498714/
- https://www.journalofcurrentoncology.org/article.asp?issn=2589-8892;year=2018;volume=1;issue=2;spage=97;epage=100;aulast=Patil
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6348784/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334632035_Cancer_Awareness_amongst_Nurses_in_a_Tertiary_Care_Hospital_in_North_Delhi_India
- https://www.crstonline.com/article.asp?issn=2590-3233;year=2021;volume=4;issue=1;spage=55;epage=60;aulast=Abbas
- https://www.crstonline.com/article.asp?issn=2590-3233;year=2020;volume=3;issue=1;spage=146;epage=147;aulast=Abbas
